
Animal Pharmaceuticals Engagement
Engagement Overview
Background
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a systemic global risk to public health and the economy, cited by the World Health Organisation (WHO) as one of the top ten global public health threats facing humanity.
An estimated 73% of global antimicrobial use by volume occurs in animal agriculture. For many animal pharmaceutical companies, antibiotics and other antimicrobials constitute a material portion of their product portfolios. The overuse and misuse of these products in animal agriculture is a significant contributor to the global risk of AMR, catalysed by manufacturing, labelling, marketing and sales practices.
The objective of this engagement is to facilitate dialogue between investors and the animal pharmaceutical sector and drive greater disclosure and clarity over how – and if – animal pharmaceutical companies are addressing the risk of AMR throughout their value chain, from factory to farm. It also seeks to explore some of the key actions the companies should take to future-proof the long-term sustainability of their antibiotic portfolios, capitalise on the growing demand for alternatives to antibiotics, and reduce the spread of AMR.
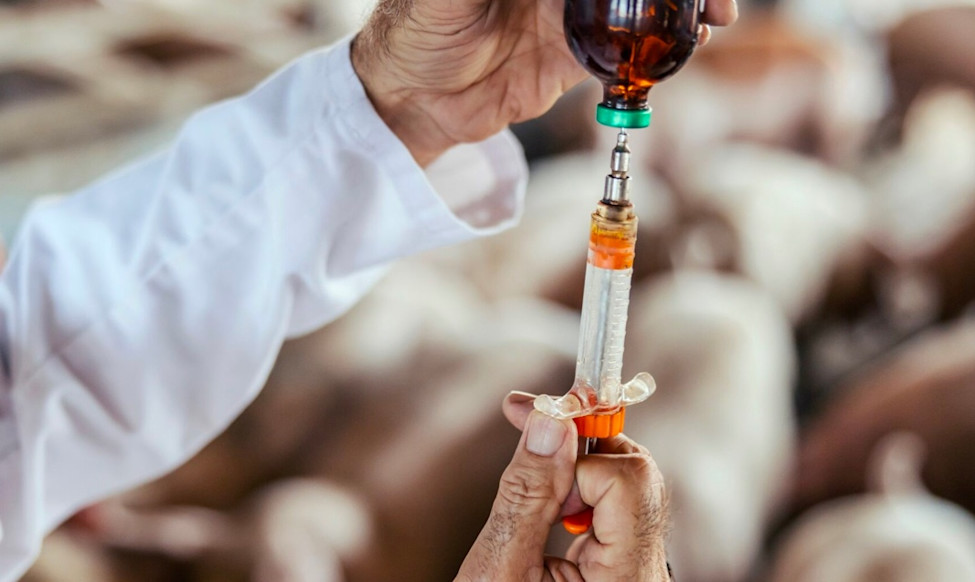
Selected Companies
This engagement targets seven of the largest publicly-listed animal pharmaceutical companies.
Material Risks
AMR is an economic, environmental, and global health risk. It is estimated that by 2050, AMR will cause up to 3.8% reduction in global GDP, an 11% loss of livestock production in LICs, and $100 trillion in economic loss.
As the relationship between antibiotic use in animal agriculture and AMR becomes ever clearer, regulators have started to respond with stricter regulation and enhanced scrutiny. Simultaneously, desire for higher animal welfare and sustainably sourced meat and dairy products is growing among consumers, alongside movement towards alternative proteins.
Forward-thinking animal pharmaceutical companies are pre-empting these changes – reducing their exposure to antibiotics for non-therapeutic purposes, investing in alternative treatment options, and looking to the pet care and companion animals market. But a coherent, strategic, business-wide approach is often lacking. Some animal pharmaceutical companies have yet to take concrete action to address the growing risk of AMR, exposing themselves to increasing regulatory, supply chain, reputational and market risks.
Investors Signed On
Phase 2 of the engagement is supported by 80 investors, representing US $17.4 trillion in combined assets, an increase of US $400 million from Phase 1.
The latest progress report, From Farms to Forks: Antibiotic Stewardship in the Animal Pharmaceutical and Quick Service Restaurant Sectors was published in May 2024.



